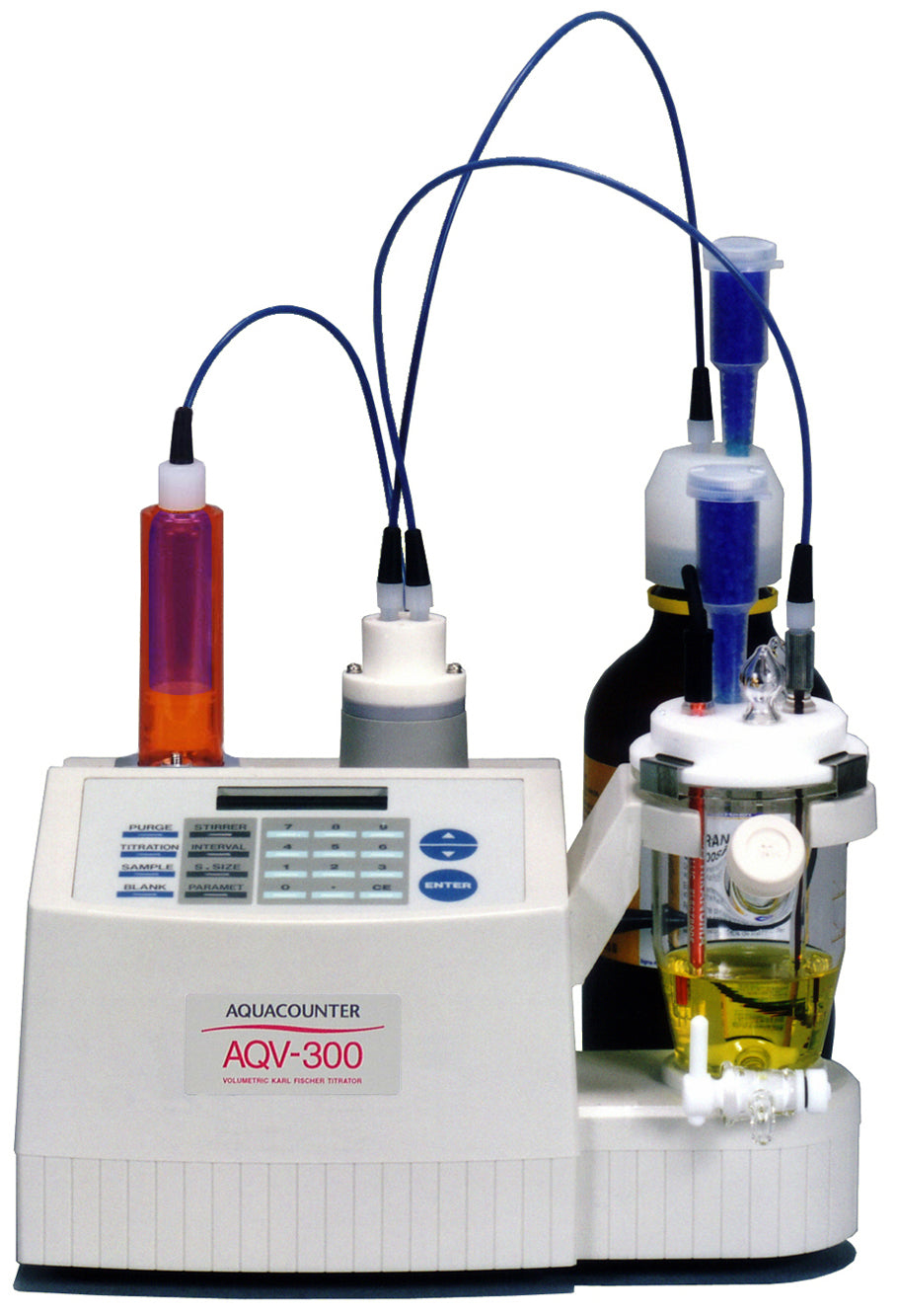
Karl Fischer & Potentiometric Titration Application Library

Determination of Tin (Sn²⁺) in solder plating solution | Autotitrator COM-A19
Tin (Sn²⁺) in solder plating solution is determined by redox titration with iodine. Solder plating solution contains Sn (II) ions, Sn (IV) ions, and acids etc. Iodine works as oxidizing agent for stannous ion. Sn (II) ions are readily oxidized by oxygen in the air to be Sn (IV) ions. The measurement environment under carbon dioxide or nitrogen gas could provide reliable results.
Sn²⁺ + I₂ → Sn⁴⁺ + 2I⁻
This report introduces a measurement example that sample is added to solution under carbon dioxide gas generated by the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate, and titrated with iodine titrant.
Sn²⁺ + I₂ → Sn⁴⁺ + 2I⁻
This report introduces a measurement example that sample is added to solution under carbon dioxide gas generated by the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate, and titrated with iodine titrant.

Quantitative determination of chromic anhydride and chromium (III) in chromium plating solution | Autotitrator COM-A19
The control and analysis of chromium plating solution are very important process for the product quality. General analytical components of the chromium plating solution are the following 5 components.
(1) Chromic anhydride (CrO₃)
(2) Chromium (III) (Cr³⁺)
(3) Sulfuric acid
(4) Fluoride ion
(5) Iron
This report introduces an example of measurement for (1) chromic anhydride and (2) chromium (III).
The measurement procedure of chromic anhydride is as follows: Take diluted sample solution and add sulfuric acid to acidify it. Accurately add a certain amount of ammonium iron (II) sulfate in an amount sufficient to react the entire amount of chromic anhydride, and react the chromic anhydride by the reaction formula (1). The unreacted ammonium iron (II) sulfate is titrated with a potassium permanganate standard solution according to reaction formula (2) to obtain chromic anhydride.
(1) Chromic anhydride (CrO₃)
(2) Chromium (III) (Cr³⁺)
(3) Sulfuric acid
(4) Fluoride ion
(5) Iron
This report introduces an example of measurement for (1) chromic anhydride and (2) chromium (III).
The measurement procedure of chromic anhydride is as follows: Take diluted sample solution and add sulfuric acid to acidify it. Accurately add a certain amount of ammonium iron (II) sulfate in an amount sufficient to react the entire amount of chromic anhydride, and react the chromic anhydride by the reaction formula (1). The unreacted ammonium iron (II) sulfate is titrated with a potassium permanganate standard solution according to reaction formula (2) to obtain chromic anhydride.

Quantitative determination of nickel chloride in nickel plating solution | Autotitrator COM-A19
The control and analysis of nickel plating solution are very important process for the product quality. Analytical components of the general nickel plating solution are 1) nickel sulfate, 2) nickel chloride, and 3) boric acid. This report introduces an example of measurement for nickel chloride in nickel plating solution determined by potentiometric titration with silver nitrate standard solution.
NiCl₂ + 2AgNO₃ → Ni (NO₃)₂ + 2AgCl
NiCl₂ + 2AgNO₃ → Ni (NO₃)₂ + 2AgCl

Determination of alkalinity in bottled water | Autotitrator COM-A19
Natural water contains alkaline components such as hydroxides and carbonates. Such water indicates alkaline pH, the alkalinity is used as an index. The alkalinity is expressed as mg/L of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) equivalent for these alkaline components. Alkalinity is divided into phenolphthalein alkalinity (P alkalinity) and total alkalinity (T alkalinity or M alkalinity) by the pH value of neutralization point.
Total amount of the hydroxides and half amount of carbonates are measured when it is titrated to about pH 8.3 with sulfuric acid titrant.
2OH⁻ + H₂SO₄ → SO₄²⁻ + 2H₂O
2CO₃²⁻ + H₂SO₄ → SO₄²⁻ + 2HCO₃⁻
All of the bicarbonates are neutralized when it is titrated successively to about pH 4.8.
HCO₃⁻ + H₂SO₄ → SO₄²⁻ + 2CO₂ + H₂O
This report introduces a measurement example for bottled water using potentiometric titration as end point detection method according to Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.
Total amount of the hydroxides and half amount of carbonates are measured when it is titrated to about pH 8.3 with sulfuric acid titrant.
2OH⁻ + H₂SO₄ → SO₄²⁻ + 2H₂O
2CO₃²⁻ + H₂SO₄ → SO₄²⁻ + 2HCO₃⁻
All of the bicarbonates are neutralized when it is titrated successively to about pH 4.8.
HCO₃⁻ + H₂SO₄ → SO₄²⁻ + 2CO₂ + H₂O
This report introduces a measurement example for bottled water using potentiometric titration as end point detection method according to Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.

Determination of residual chlorine in tap water | Autotitrator COM-A19
Tap water chlorinated from lake water and river water contains residual chlorine. The residual chlorine is sometimes called available chlorine, which is composed of free residual chlorine and combined residual chlorine.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water adopts the following methods as determination method for residual chlorine.
・Dimethyl -p- phenylenediamine (DPD) method ………………………………………………Colorimetric method
・Dimethyl -p- phenylenediamine (DPD) titration method………………………………………Titration method
・Amperometric titration method (Titration method with phenylarsenoxide solution) ………Titration method
・Iodometric titration method………………………………………………………………………Titration method
This report introduces an example for determination of residual chlorine in tap water with iodometric titration method.
Residual chlorine oxidizes potassium iodide in acidic solution to generate free iodine.
Cl₂ + 2I⁻ → I₂ + 2Cl⁻
The generate iodine is potentiometrically titrated with sodium thiosulfate standard solution.
I₂ + 2Na₂S₂O₃ → 2NaI + Na₂S₄O₆
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water adopts the following methods as determination method for residual chlorine.
・Dimethyl -p- phenylenediamine (DPD) method ………………………………………………Colorimetric method
・Dimethyl -p- phenylenediamine (DPD) titration method………………………………………Titration method
・Amperometric titration method (Titration method with phenylarsenoxide solution) ………Titration method
・Iodometric titration method………………………………………………………………………Titration method
This report introduces an example for determination of residual chlorine in tap water with iodometric titration method.
Residual chlorine oxidizes potassium iodide in acidic solution to generate free iodine.
Cl₂ + 2I⁻ → I₂ + 2Cl⁻
The generate iodine is potentiometrically titrated with sodium thiosulfate standard solution.
I₂ + 2Na₂S₂O₃ → 2NaI + Na₂S₄O₆

Calcium hardness in tap water | Autotitrator COM-A19
There are determination methods for hardness in tap water as follows: (1) Total hardness defined as the sum of calcium and magnesium ion converted to mg/L as calcium carbonate (CaCO3), (2) Calcium hardness determined by calcium ion concentration.
The measurement method for calcium hardness is similar to that of total hardness. Adjust the pH of sample water to higher than pH 12 with sodium hydroxide to mask the reaction of magnesium and EDTA. Start titration with 2-hydroxy-1-(2-hydroxy-4-sulfo-1-naphthylazo)-3-naphthoic acid (NN) indicator. Its color changes from red to blue.
CaCO₃ + Na₂EDTA → CaEDTA + Na₂CO₃
This report introduces an example of calcium hardness measurement for tap water with photometric titration method using EDTA standard solution according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.
The measurement method for calcium hardness is similar to that of total hardness. Adjust the pH of sample water to higher than pH 12 with sodium hydroxide to mask the reaction of magnesium and EDTA. Start titration with 2-hydroxy-1-(2-hydroxy-4-sulfo-1-naphthylazo)-3-naphthoic acid (NN) indicator. Its color changes from red to blue.
CaCO₃ + Na₂EDTA → CaEDTA + Na₂CO₃
This report introduces an example of calcium hardness measurement for tap water with photometric titration method using EDTA standard solution according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.

Total hardness in tap water | Autotitrator COM-A19
Hardness in water is total amount of calcium and magnesium ion in water converted to mg/L of comparable calcium carbonate. “Hardness” has the following types:
(1) Total hardness Total amount of calcium and magnesium ions
(2) Calcium hardness Calcium ion
(3) Magnesium hardness (Total hardness) – (Calcium hardness)
(4) Non-carbonate hardness (Permanent hardness)
(5) Carbonate hardness (Temporary hardness)
These are stipulated in some applicable standard such as Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Standard Methods of Analysis for Hygienic Chemists, and JIS K0101 Testing methods for industrial water etc.
This report introduces an example for determination of total hardness in tap water with photometric titration method using EDTA standard solution according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.
Take 100 mL of sample and add 1 mL of 0.01 mol/L magnesium chloride, 2 mL ammonia buffer, and 0.2 mL of EBT indicator. Titrate with 0.01 mol/L EDTA standard solution (red →blue color). Perform the same procedure for 100 mL of DI water instead of sample as blank measurement.
CaCO₃ + Na₂EDTA → Ca-EDTA + Na₂CO₃
MgCO₃ + Na₂EDTA → Mg-EDTA + Na₂CO₃
(1) Total hardness Total amount of calcium and magnesium ions
(2) Calcium hardness Calcium ion
(3) Magnesium hardness (Total hardness) – (Calcium hardness)
(4) Non-carbonate hardness (Permanent hardness)
(5) Carbonate hardness (Temporary hardness)
These are stipulated in some applicable standard such as Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Standard Methods of Analysis for Hygienic Chemists, and JIS K0101 Testing methods for industrial water etc.
This report introduces an example for determination of total hardness in tap water with photometric titration method using EDTA standard solution according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.
Take 100 mL of sample and add 1 mL of 0.01 mol/L magnesium chloride, 2 mL ammonia buffer, and 0.2 mL of EBT indicator. Titrate with 0.01 mol/L EDTA standard solution (red →blue color). Perform the same procedure for 100 mL of DI water instead of sample as blank measurement.
CaCO₃ + Na₂EDTA → Ca-EDTA + Na₂CO₃
MgCO₃ + Na₂EDTA → Mg-EDTA + Na₂CO₃

Quantitative determination of chloride ions in tap water | Autotitrator COM-A19
Quantitative determination for chloride ions in tap water is stipulated in Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, and Standard Methods of Analysis for Hygienic Chemists, etc. A small amount of chloride ion is contained in natural water, it is said to increase due to contamination of domestic drainage, industrial drainage, and farming drainage, etc. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water adopts ion exchange chromatograph method and Mohr method (titration method) as the chloride quantitative determination method. The detection limit for ion exchange chromatograph method is 0.2 mg/L. Mohr method is generally applied for samples including chloride ions in mg/L or more. This report introduces the Mohr method with precipitation titration, which quantifies chlorides by potentiometric titration with silver indicator electrode instead of the color indicator titration described in Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.
100 mL of the sample water is collected and acidified with nitric acid for potentiometric titration with silver nitrate titrant.
Cl⁻ + AgNO₃ → AgCl↓ + NO₃⁻
100 mL of the sample water is collected and acidified with nitric acid for potentiometric titration with silver nitrate titrant.
Cl⁻ + AgNO₃ → AgCl↓ + NO₃⁻

Standardization of benzethonium chloride standard solution | Autotitrator COM-A19
The determination method of anion surfactant uses a cation surfactant, with an opposite charge, as the titrant. The end point is the point at which the charge becomes neutral due to the reaction between the anion and the cation. Benzethonium chloride is used as the cation standard solution.
This report introduces a method for standardization of benzethonium chloride standard solution. Sodium dodecyl sulfate is used for standard solution. First, determine the purity of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Add diluted sulfuric acid to sodium dodecyl sulfate, heat to reflux, and then titrate with sodium hydroxide standard solution.
Subsequently, prepare the standard solution of sodium dodecyl sulfate whose purity has been determined, and standardize the benzethonium chloride standard solution with titration against sodium dodecyl sulfate standard solution.
This report introduces a method for standardization of benzethonium chloride standard solution. Sodium dodecyl sulfate is used for standard solution. First, determine the purity of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Add diluted sulfuric acid to sodium dodecyl sulfate, heat to reflux, and then titrate with sodium hydroxide standard solution.
Subsequently, prepare the standard solution of sodium dodecyl sulfate whose purity has been determined, and standardize the benzethonium chloride standard solution with titration against sodium dodecyl sulfate standard solution.

Quantitative determination of sodium sulfate in bath additive | Autotitrator
The precipitation titration using lead ion-selective electrode achieves the measurement of sulfate ions. Lead sulfate is generated by adding lead nitrate to sulfate ion. The potential reading with lead ion-selective electrode differs depending on the concentration of sulfate ion in sample solution. The maximum change in potential is observed when it reaches the equivalent point of sulfate and lead ions. The concentration of sulfate ion is determined by the titrant volume consumed until it reaches the inflection point.
SO₄²- + Pb(NO₃)₂ → PbSO₄ + 2NO₃-
This report introduces an example of the measurement for sulfate ion in bath additive with using lead ion-selective electrode.
SO₄²- + Pb(NO₃)₂ → PbSO₄ + 2NO₃-
This report introduces an example of the measurement for sulfate ion in bath additive with using lead ion-selective electrode.

Determination of anion surfactant in detergent | Autotitrator
The determination method of anion surfactant uses a cation surfactant with an opposite charge as the titrant. The end point is the point at which the charge becomes neutral due to the reaction between the anion and the cation. Benzethonium chloride is used as the cation standard solution.
This report introduces an example of determination of anion surfactant sodium alkylbenzene sulfonate in detergent by potentiometric titration using a surfactant electrode as an indicator electrode.
This report introduces an example of determination of anion surfactant sodium alkylbenzene sulfonate in detergent by potentiometric titration using a surfactant electrode as an indicator electrode.
Quantitative determination of sodium citrate | Autotitrator
Sodium citrate is used as anticaking agent for blood in pharmaceutical field. Quantitative determination method for sodium citrate is stipulated in Japanese Pharmacopoeia.
This report introduces an example of potentiometric titration for sodium citrate that well-dried sample is dissolved in acetic acid, then it is titrated with perchloric acid – acetic acid standard solution.
C₆H₅Na₃O₇ + 3HClO₄ → C₆H₈O₇ + 3NaClO₄
This report introduces an example of potentiometric titration for sodium citrate that well-dried sample is dissolved in acetic acid, then it is titrated with perchloric acid – acetic acid standard solution.
C₆H₅Na₃O₇ + 3HClO₄ → C₆H₈O₇ + 3NaClO₄



