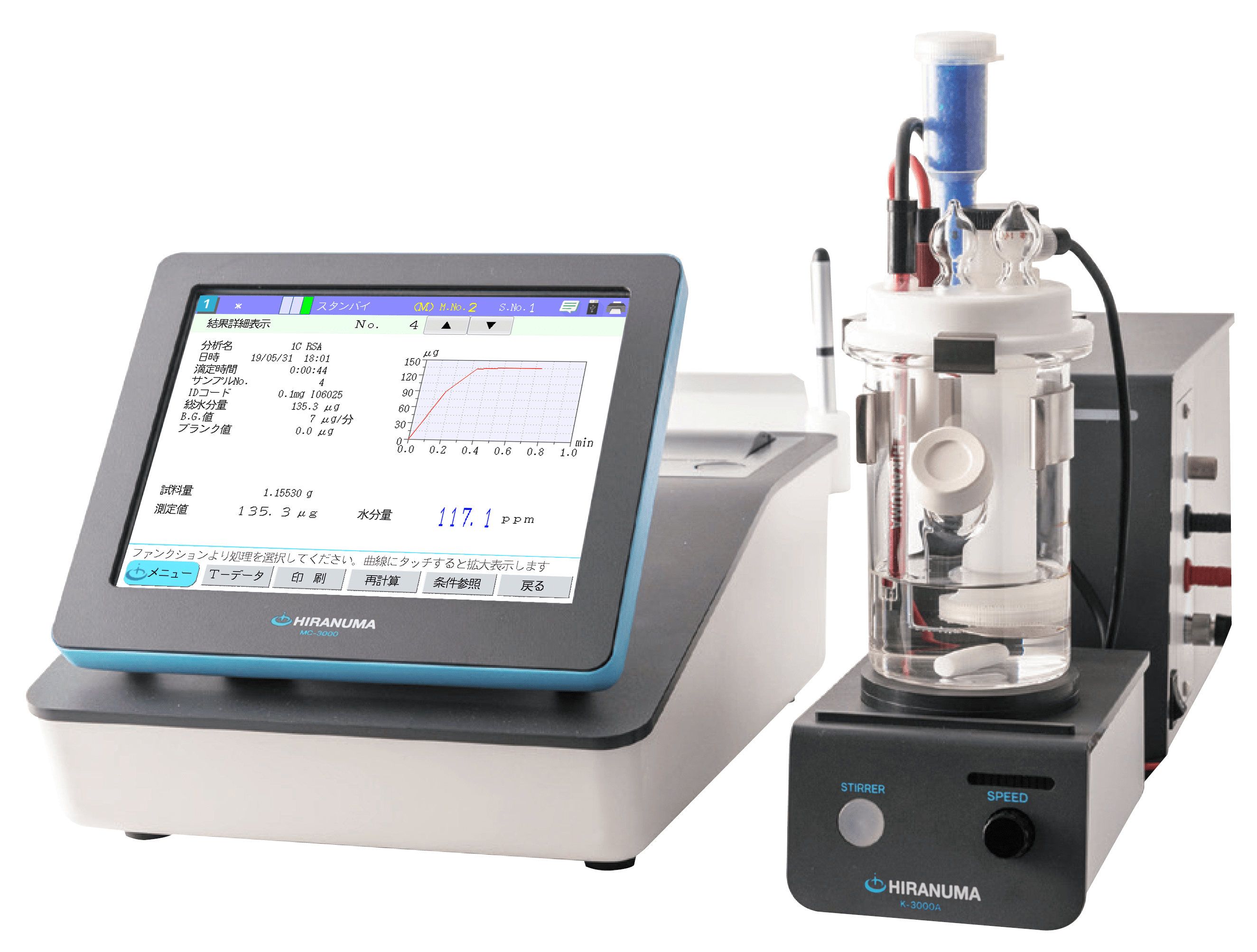
| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Automatic Titrator | Data No. | G1 | Apr. 5,2019 |
| Metals | Quantitative determination of zinc ion |
1. Abstract
Zinc ion can be readily determined by chelatometric titration. The titration with EDTA can be performed at the wide pH region (pH 4.5 ~ 10). The stability constant of Zn-EDTA complex is relatively large,1 there are a lot of highly sensitive indicator reagents for this titration. The report introduces an example that the sample adjusted to pH around 5.3 is photometrically titrated with EDTA titrant using XO indicator (red purple →yellow).
| Zn²⁺ + Na₂EDTA → Zn-EDTA + 2Na⁺ |
2. Configuration of instruments and Reagents
| (1) | Configuration of instruments | ||
| Main unit | : | Hiranuma Automatic Titrator COM series (w/ Photometric titrator unit type M) with 530 nm optical filter |
|
| (2) | Reagent | ||
| Titrant | : | 0.1 mol/L EDTA standard solution | |
| Buffer solution | : | Acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution (pH 5 ~ 5.3) | |
| Indicator | : | 1 mL of XO indicator (0.05 % solution) | |
3. Measurement procedure
| (1) | Dispense 5 mL of sample into a 100 mL beaker with a volumetric pipette. |
| (2) | Add about 60 mL of DI water. |
| (3) | Add 5 mL of acetic acid- sodium acetate buffer solution. |
| (4) | Add 1 mL of XO indicator. |
| (5) | Immerse photometric probe into sample solution and titrate with 0.1 mol/L EDTA standard solution. |
4. Measurement conditions and results
Examples of titration conditions

Measurement results
| Number of measurement |
Size (mL) |
Titrant volume(mL) |
Zinc ion Concentration (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 5.348 | 7.030 |
| 2 | 5 | 5.349 | 7.029 |
| 3 | 5 | 5.348 | 7.030 |
| Statistic calculation |
Avg. | 7.03 g/L | |
| SD | 0.0006 g/L | ||
| RSD | 0.008 % | ||
Example of titration curve

5. Note
| (1) | Measurement condition |
| The color of indicator reagent suddenly changes at the endpoint, therefore the minimum increment (0.05 mL in this report) titration without “Del K” control allows to get good results. The function “CP mL” can reduce the measurement time by continuously adding 0.5 ~ 1 mL smaller titrant volume than the volume consumed until the endpoint. The “Method” on condition parameter is set to “B Cross” because the endpoint is defined as the point where the color change of the indicator is completed. | |
| (2) | Other titration methods for zinc ion determination |
| There are some other chelatometric titration methods for zinc ion determination depending on indicator reagents and suitable pH regions. i) Indicator reagents BT indicator (red → blue) is often used at alkaline pH besides XO indicator (can be used at acidic condition) used in this report. It is usable at the pH region from 7 to 10. However, please note that the color change is interfered by Cu2+, Co2+, and Ni2+ ions when they are contained in the sample. ii) Interfering ions There is no interference on the measurement even if alkali metal is contained in the sample. Ni2+, Fe3+, and Al3+ ions could interfere the color change of indicator reagent. The small amount of Al3+ ion does not interfere the measurement because the reaction rate is slow under the low concentration condition. Cu2+ ion interfere the measurement but the addition of thiourea or sodium thiosulfate can mask the Cu2+ ion. |
| Keywords: | Zinc ion, Photometric titration, Chelatometric titration |
| References: | (1) K. Ueno, “Chelatometry”, 1987, Nankodo, Tokyo. |
*Some measurement would not be possible depending on optional configuration of system.