| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Karl Fischer Titrator | Data No. | KF14 | Nov.29. 2018 |
| Water contents | Ketones and Aldehydes – KF Volumetry, Direct-Injection Methyl ethyl ketone, Acetone, and Cyclohexanone |
1. Abstract
Water contents of ketones and aldehydes could be determined by Karl Fischer volumetric titrator. In volumetric titration, titrant have a factor which is the capacity to react with water per 1 mL of titrant. Factor is pre-determined before sample measurement and water content of sample is calculated from consumed titrant volume by sample measurement.
When the sample is liquid, generally sample is measured by direct injection into the titration cell. Dehydrated methanol is generally used for titration solvent. However, in the measurement of ketones and aldehydes, since these react with methanol to produce water, the measurement result tends to be higher than the true value (formula (1)).
R₂CO + 2CH₃OH → R₂C(OCH₃)₂ + H₂O ・・・(1)
For above reason, Karl Fischer reagent without methanol should be used for water determination of ketones and aldehydes. There are commercially available reagents with a special composition for ketones and aldehydes. This chapter introduces an example for the water determination in methyl ethyl ketone, acetone and cyclohexanone with water added to them to 1 %. These samples are often used as paint solvents, raw materials of adhesives, and synthetic resins.
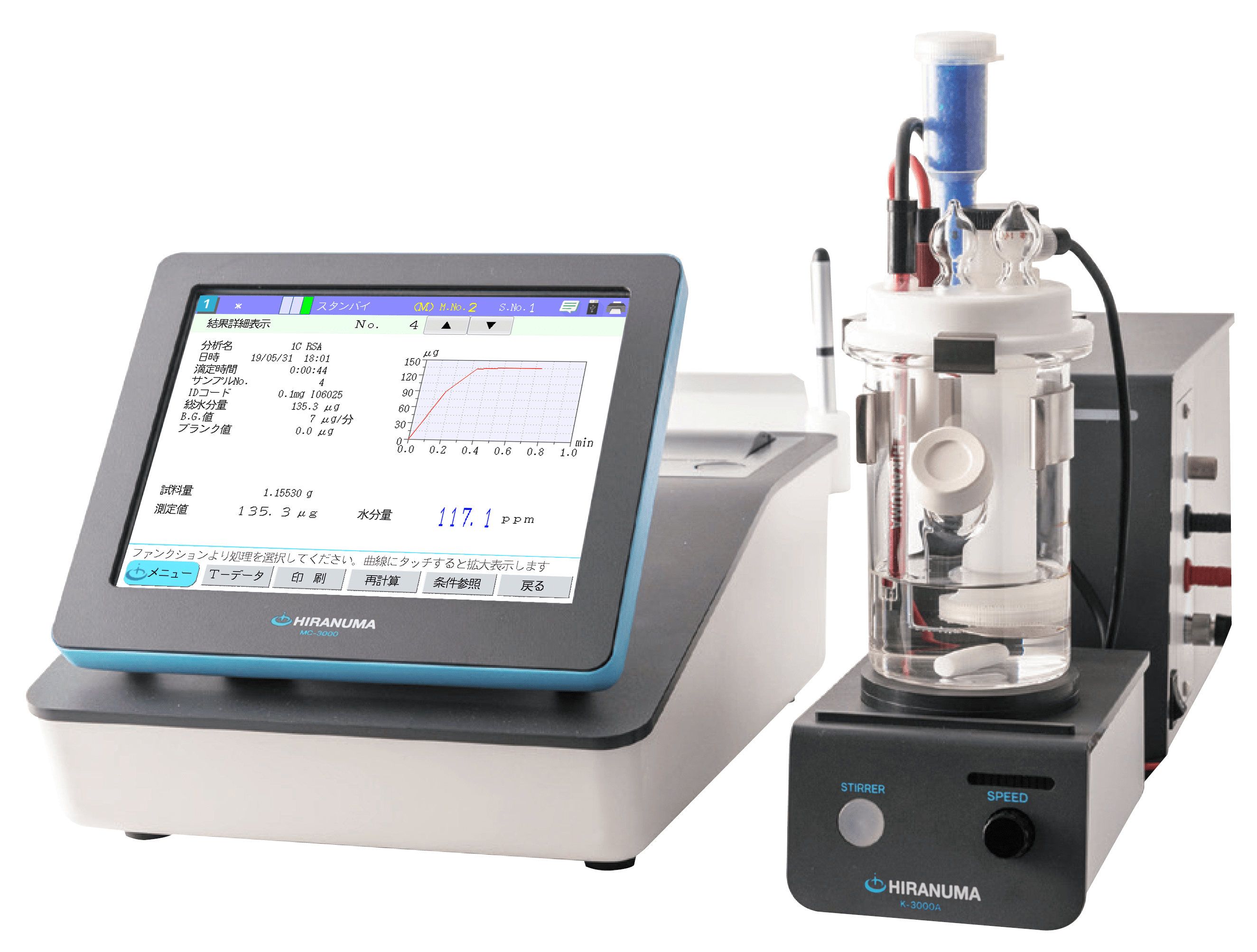
2. Apparatus and Reagents
| (1) | Apparatus | ||
| Titrator | : | HIRANUMA Karl Fischer Volumetric titrator AQV-series or MOIVO-A19 | |
| Titration cell | : | Standard Cell | |
| (2) | Reagents | ||
| Titrant | : | HYDRANAL Composite 5K | |
| Titration solvent | : | HYDRANAL Working Medium K |
3. Procedure
| (1) | Fill 50 mL of titration solvent into the titration cell as shown in Fig.3.1. |
| (2) | Start blanking to attain stable background. |
| (3) | Wash the syringe with sample. |
| (4) | Draw the sample into syringe and then weigh the syringe. |
| (5) | Inject sample from rubber septum of titration cell as shown in Fig.3.2. |
| (6) | Start titration. Measurement parameter is shown in Table 4.1. |
| (7) | Weigh the syringe again and then set the difference of weight to sample size. |

Fig.3.1 Preparation of the reagents

Fig.3.2 Injection of sample
4. Parameters and results
Table 4.1. Parameter.
| Condition File | ||
| Cal Mode | 0:Sample weight(net) | |
| X=(H-b)xFx1000/SIZE | ||
| Interval Time | 30 | sec |
| Max Volume | 20 | mL |
| Min Feed Vol. | 0.01 | mL |
| S.Timer | 0 | min |
| KF Factor | 5.4839 | mg/mL |
| KF Buret No. | 1 | |
| KF Speed(OUT) | 12 | mL/min |
| KF Speed(IN) | 24 | mL/min |
| Back Ground | OFF | |
| Sample Size Input | Every Time | |
| Blank Value | 0 | mL |
| Unit Mode | AUTO | |
| E.P Detection | uA | |
| Solvent | S,O,CE | |
| C.P Level | 150 | µA |
| E.P Level | 200 | µA |
| Auto Interval | 0 | g |
Table 4.2 Results of water content measurement in ketones
| Sample | Sample size (g) |
Titer (mL) |
Water (mg) |
Water content (%) |
Statistics result | |
| Methyl ethyl ketone | 0.5410 | 1.04 | 5.759 | 1.0645 | Avg. | 1.062 % |
| 0.4792 | 0.92 | 5.095 | 1.0632 | SD | 0.003 % | |
| 0.5652 | 1.08 | 5.981 | 1.0582 | RSD | 0.31 % | |
| Acetone | 0.4925 | 0.91 | 5.039 | 1.0231 | Avg. | 1.025 % |
| 0.5003 | 0.93 | 5.150 | 1.0294 | SD | 0.004 % | |
| 0.4171 | 0.77 | 4.264 | 1.0223 | RSD | 0.38 % | |
| Cyclohexanone | 0.4023 | 0.74 | 4.098 | 1.0186 | Avg. | 1.021 % |
| 0.3848 | 0.71 | 3.932 | 1.0218 | SD | 0.003 % | |
| 0.3841 | 0.71 | 3.932 | 1.0237 | RSD | 0.25 % | |
5. Note
| (1) | When the side reaction cannot be suppressed even though you use reagent for ketones, phenomena such as unstable blanking or undetectable endpoint can be obtained. In that case, it may be improved by reducing the amount of sample or replacing titration solvent with new one. |
| (2) | Sampling tools should be dried up well before use. |
| (3) | Purge and fill the titrant to fill it homogeneously into the buret. |