| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Karl Fischer Titrator | Data No. | KF6 | Nov.29. 2018 |
| Water contents | Amines |
1. Abstract
Water content of amines could be determined by Karl Fischer coulometric titrator. In coulometric titration, iodine of Karl Fischer reagent is generated by electrolysis and generated iodine quantitatively reacts with water. Reaction formula is described below.
H₂O + I₂ + SO₂ + 3RN + CH₃OH → 2RN・HI + RN・HSO₄CH₃
2RN・HI → I₂ + 2RN + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
The amines change anode solution pH to basic. In the case of an amine with stronger basicity than benzylamine (pKa = 9.34¹)) as a guideline, there are such effects as the end point becomes unclear. Therefore, when measuring a strongly basic amine, add a neutralizing agent to the anode solution beforehand to suppress the influence of undesirable effect caused by adding the sample. This application introduces an example for the water determination in cyclohexylamine(liquid), diethanolamine(liquid) and imidazole(solid). Reference
1) H. K. Hall, J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1957) 79 5441.
2. Apparatus and Reagents
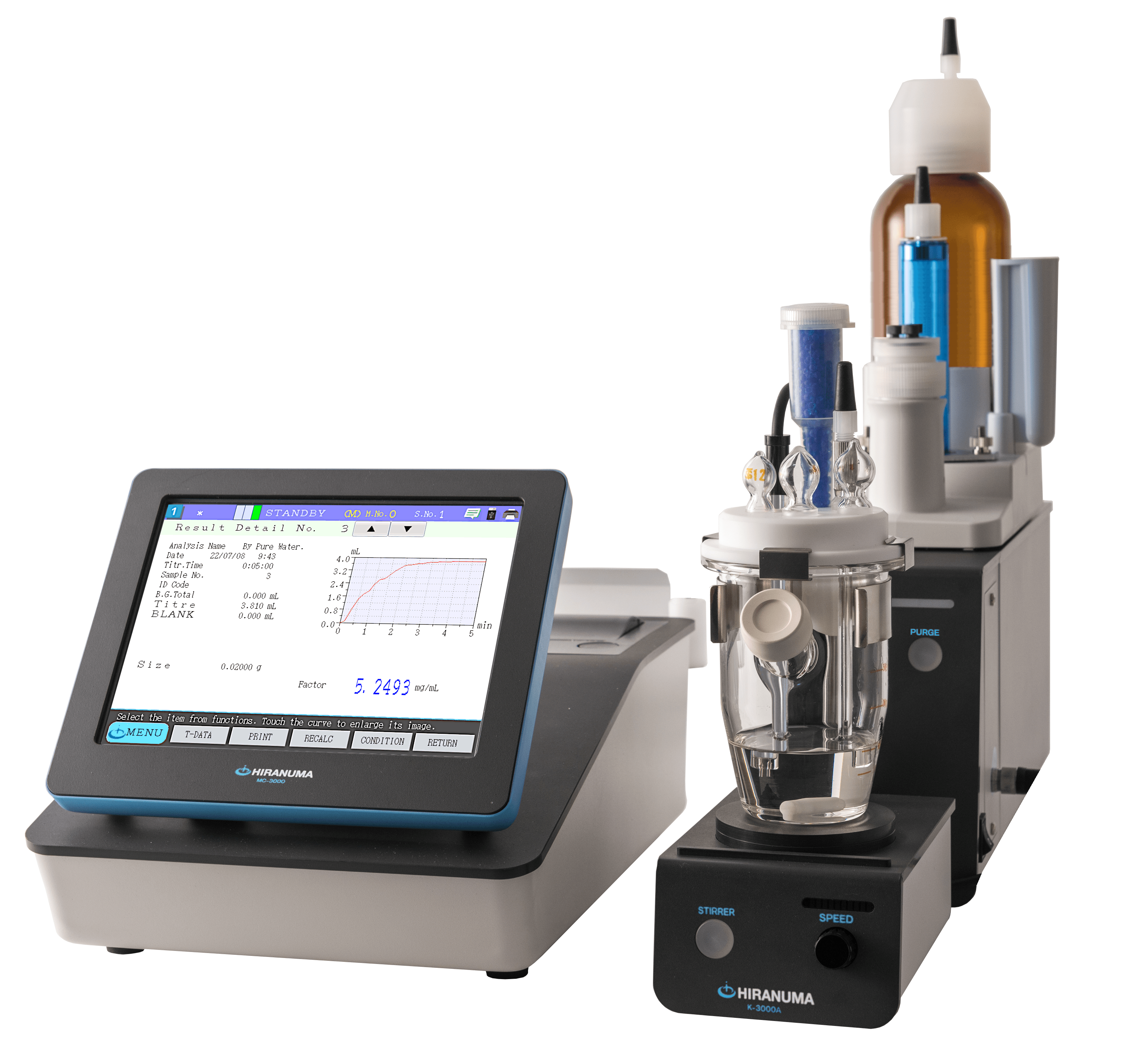
| (1) | Apparatus | ||
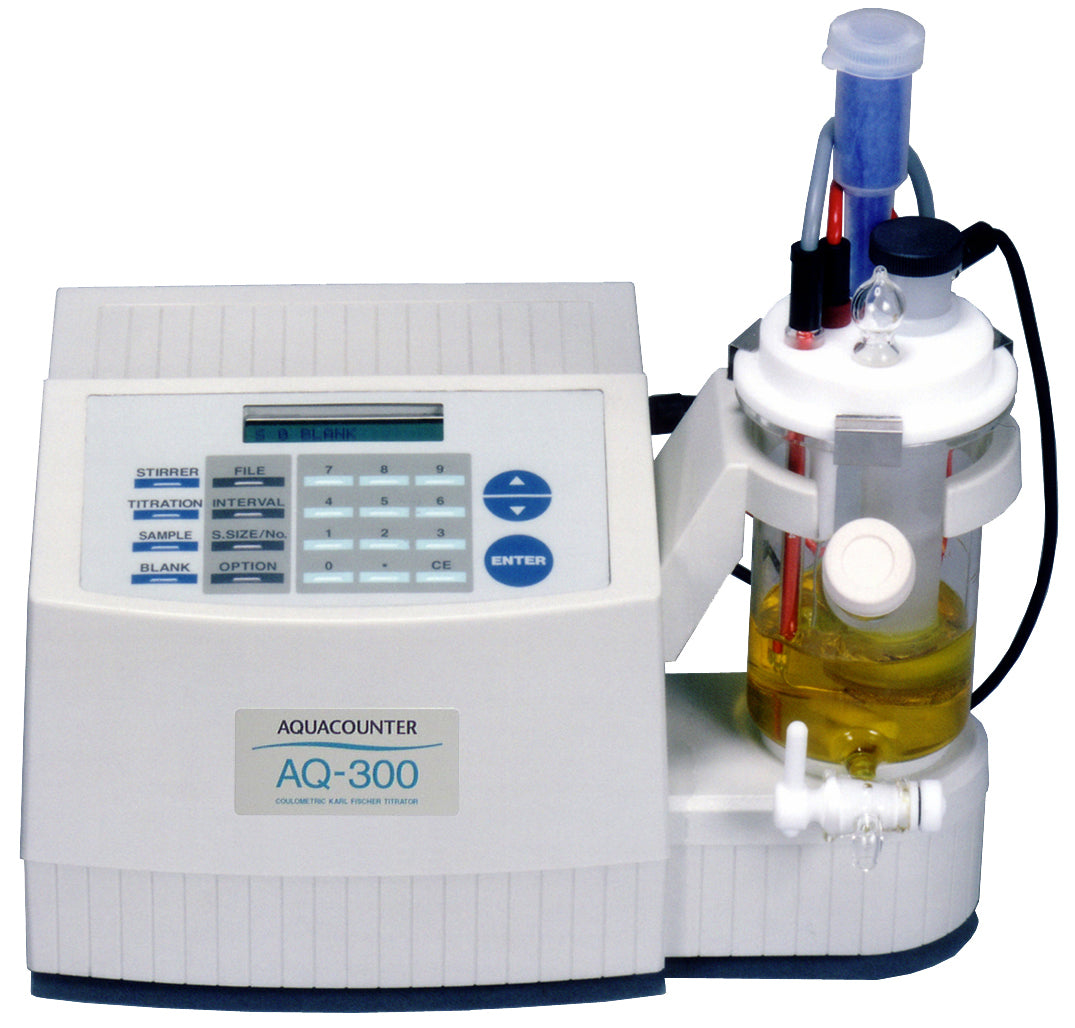
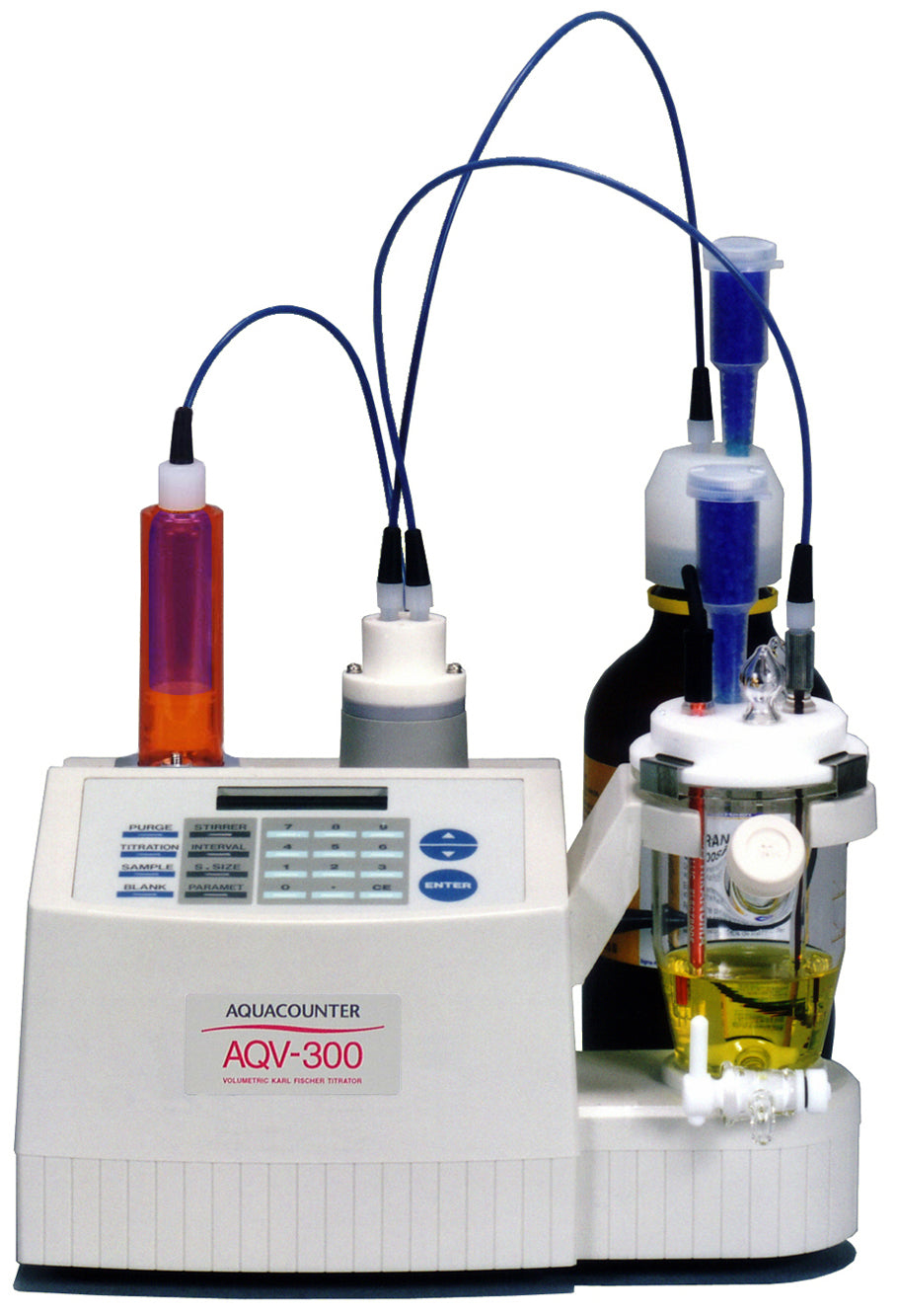
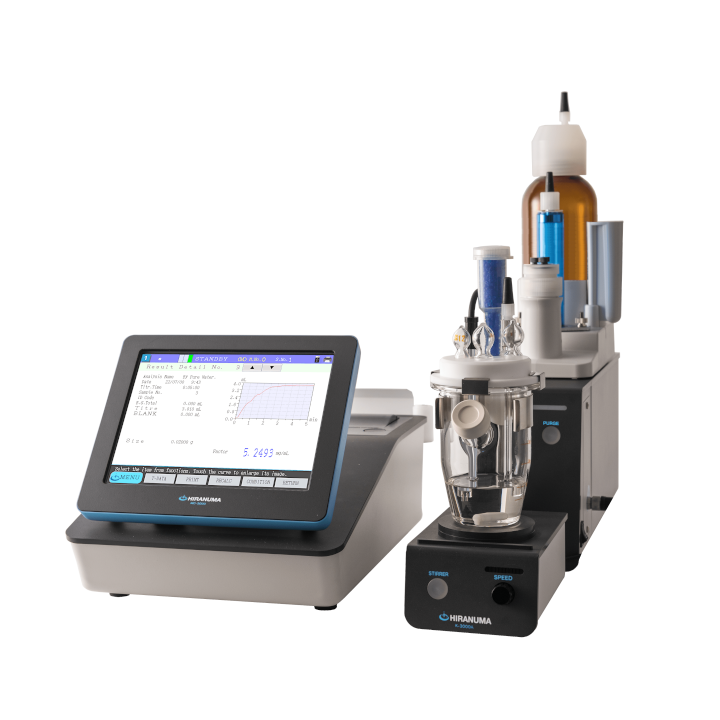
| Titrator | : | HIRANUMA Karl Fischer Coulometric titrator AQ-series or MOICO-A19 | |
| Electrolytic cell | : | Standard Cell Fritless Cell (No cathode solution required) |
|
| (2) | Reagents | ||
| Anode solution | : | HYDRANAL Coulomat AG (Honeywell) | |
| Cathode solution | : | HYDRANAL Coulomat CG (Honeywell) | |
| Neutralizing agent | : | Benzoic acid |
3. Procedure
3.1. Measurement of liquid sample
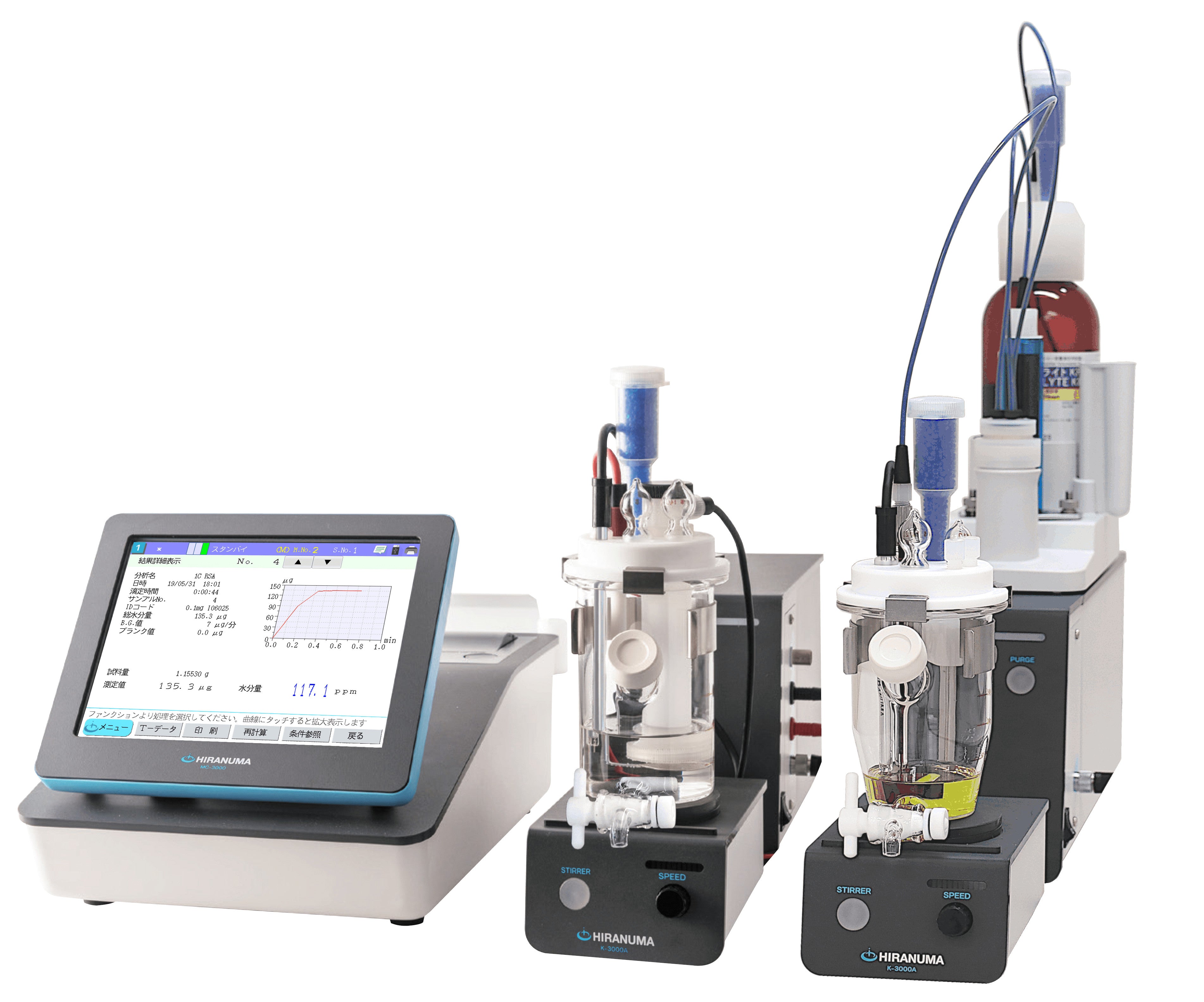
| (1) | Add 10 g of benzoic acid and 100 mL of anode solution in anode compartment of titration cell as shown in Fig.3.1. Add one ampoule of cathode solution into the cathode compartment. When fritless cell is used, cathode solution is not necessary. Stir the anode solution to dissolve benzoic acid. |
| (2) | Start blanking to attain stable background. |
| (3) | Wash the syringe with sample. |
| (4) | Draw the sample into syringe and then weigh the syringe. |
| (5) | Inject sample from rubber septum of electrolytic cell as shown in Fig.3.2. |
| (6) | Start titration. Measurement parameter is shown in Table 4.1. |
| (7) | Weigh the syringe again and then set the difference of weight to sample size. |
3.2. Measurement of solid sample
| (1) | Add 10 g of benzoic acid and 100 mL of anode solution in anode compartment of titration cell as shown in Fig.3.1. Add one ampoule of cathode solution into the cathode compartment. Stir the anode solution to dissolve benzoic acid. |
| (2) | Start blanking to attain stable background. |
| (3) | Put a sample container, powder funnel and spoon on the balance. Record its read (S₁ [g]). |
| (4) | Open the glass stopper of titration cell lid to introduce the sample with powder funnel as shown in Fig.3.3. |
| (5) | Start titration. Measurement parameter is shown in Table 4.1. |
| (6) | Weigh the sample container, powder funnel and spoon again and record its read (S₂ [g]). The difference of (S₁-S₂ [g]) is set as sample size. |
| (7) | Blank measurement is also performed with same procedure except for sample addition. |

Fig.3.1. Preparation of the reagents. (Standard Cell)

Fig.3.2. Injection of liquid sample.

Fig.3.3. Addition of solid sample.
4. Parameters and results
Table 4.1. Parameters
| Condition File | ||
| Cal Mode | 0:Sample weight(net) | |
| X=(H₂O-BLANK)/SIZE | ||
| Interval Time | 20 | sec |
| Current | SLOW | |
| S-Timer* | 0 | min |
| Blank Value | 0 | µg |
| Unit Mode | AUTO | |
| Auto Interval | 0 | g |
| Minimum Count | 5 | µg |
| Back Ground | ON | |
| Sample Size Input | Every Time | |
| Cell Type | Standard/Fritless |
* Dissolving time for solid sample set on S.Timer
Table 4.2. Results of water content measurement in amines
| Sample | Reagent | Cell | Sample Size (g) |
Water (μg) |
Water Content (%) |
Statistics Results | |
| Cyclohexylamine | AG | Standard | 0.1742 | 235.5 | 0.1352 | Avg. | 0.1350 % |
| + Benzoic acid | 0.1790 | 239.5 | 0.1338 | SD | 0.8 % | ||
| / CG | 0.1941 | 263.8 | 0.1359 | RSD | 0.8 % | ||
| AG | Fritless | 0.2232 | 307.1 | 0.1376 | Avg. | 0.1367 % | |
| + Benzoic acid | 0.2694 | 366.1 | 0.1359 | SD | 0.0009 % | ||
| 0.2305 | 315.0 | 0.1367 | RSD | 0.6 % | |||
| Diethanolamine | AG | Standard | 0.2465 | 478.1 | 0.1940 | Avg. | 0.1923 % |
| / CG | 0.2877 | 557.8 | 0.1939 | SD | 0.0029 % | ||
| 0.2340 | 442.3 | 0.1890 | RSD | 1.5 % | |||
| AG | Fritless | 0.2361 | 476.8 | 0.2019 | Avg. | 0.2020 % | |
| 0.2473 | 505.0 | 0.2042 | SD | 0.0022 % | |||
| 0.2696 | 538.9 | 0.1999 | RSD | 1.1 % | |||
| Imidazole | AG | Standard | 0.4219 | 643.7 | 0.1526 | Avg. | 0.1524 % |
| / CG | 0.6296 | 964.0 | 0.1531 | SD | 0.0008 % | ||
| 0.3946 | 597.7 | 0.1515 | RSD | 0.5 % | |||
| AG | Fritless | 0.2336 | 371.5 | 0.1590 | Avg. | 0.1586 % | |
| 0.3491 | 547.7 | 0.1569 | SD | 0.0015 % | |||
| 0.2551 | 407.6 | 0.1598 | RSD | 0.9 % | |||
5. Note
| (1) | When the side reaction of amine cannot be suppressed even though you use neutralizing agent, phenomena such as unstable blanking or undetectable endpoint can be obtained. In that case, it may be improved by reducing the amount of sample or replacing titration solvent with new one. |
| (2) | Since aromatic amines react with methanol to form water, it is necessary to use reagent for ketone. |
| (3) | The optimized electrolysis control for fritless cell of AQ series released after 2009 improves the measurement accuracy of fritless cell. It can be used with the evaporator as well. Suitable reagent for fritless cell is required. For example, Hydranal coulomat AG and AG-Oven are compatible with fritless cell. |
| Keywords: | Karl Fischer, Coulometric titration, Amine |