| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Automatic Titrator | Data No. | D1 | Nov. 14,2018 |
| Environment | Quantitative determination of chloride ions in tap water |
1. Abstract
Quantitative determination for chloride ions in tap water is stipulated in Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, and Standard Methods of Analysis for Hygienic Chemists, etc. A small amount of chloride ion is contained in natural water, it is said to increase due to contamination of domestic drainage, industrial drainage, and farming drainage, etc. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water adopts ion exchange chromatograph method and Mohr method (titration method) as the chloride quantitative determination method. The detection limit for ion exchange chromatograph method is 0.2 mg/L. Mohr method is generally applied for samples including chloride ions in mg/L or more. This report introduces the Mohr method with precipitation titration, which quantifies chlorides by potentiometric titration with silver indicator electrode instead of the color indicator titration described in Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.
100 mL of the sample water is collected and acidified with nitric acid for potentiometric titration with silver nitrate titrant.
| Cl⁻ + AgNO₃ → AgCl↓ + NO₃⁻ |
2. Configuration of instruments and Reagents
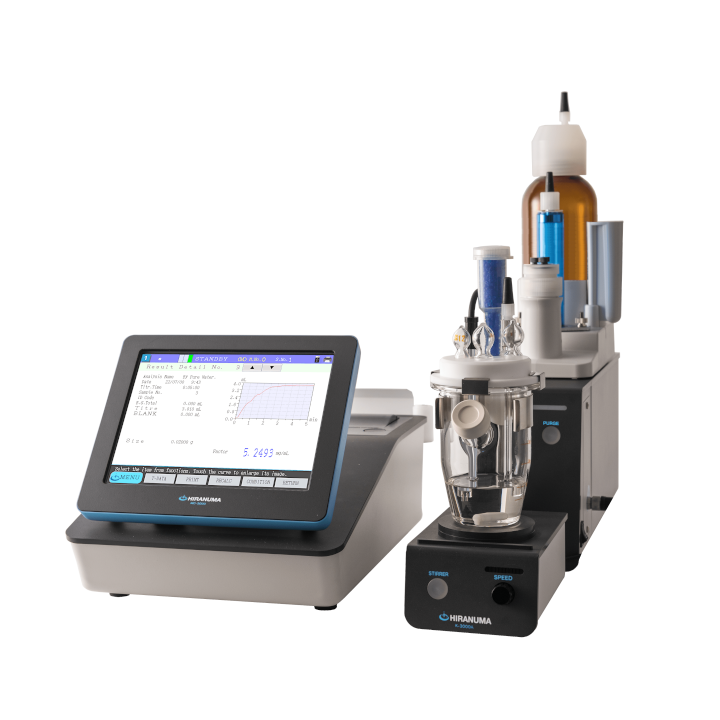
| (1) | Configuration of instruments | ||
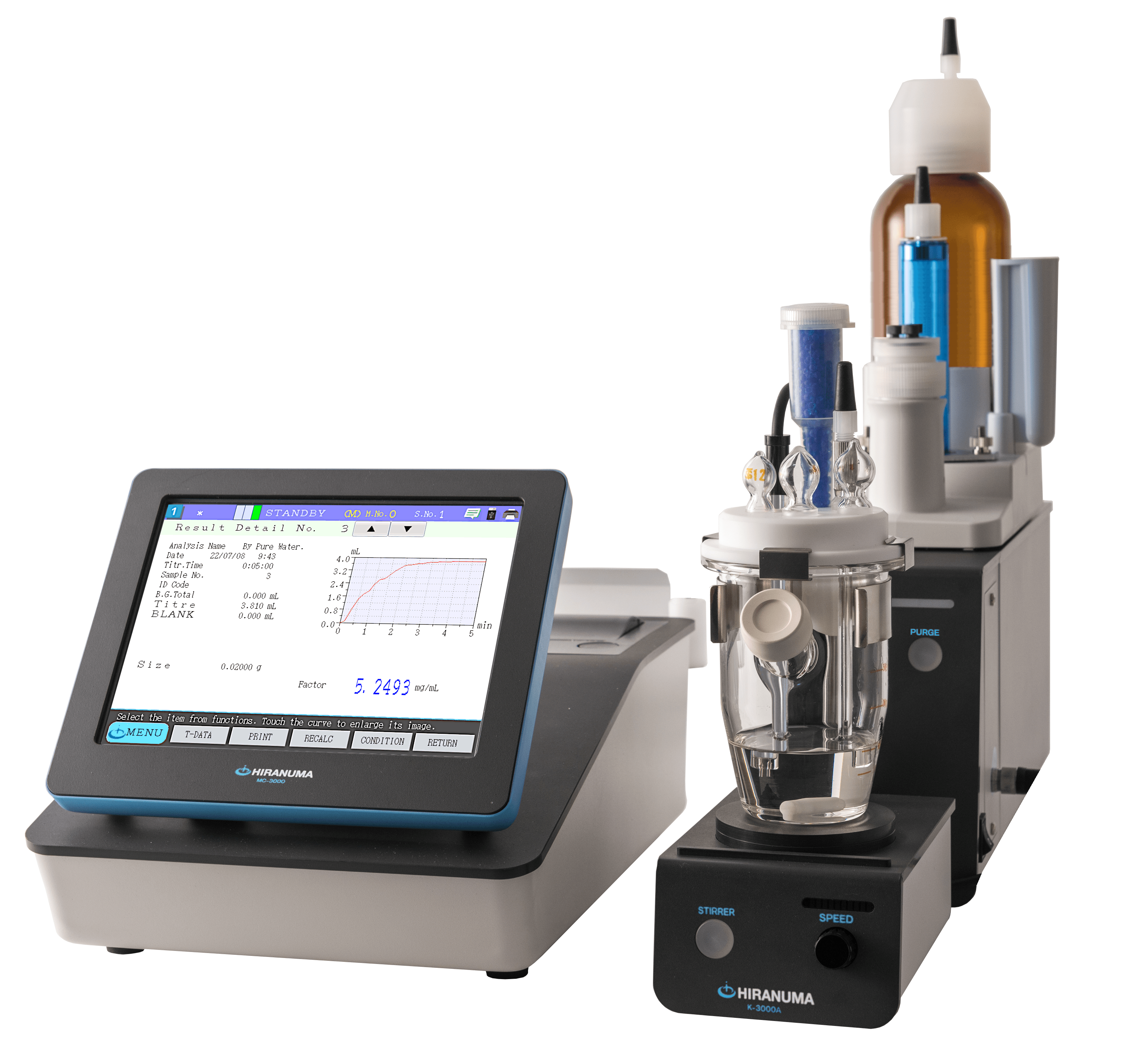
| Main unit | : | Automatic Titrator COM Series | |
| Electrodes | : | Silver combination electrode AGR-811Z (Double Junction Type) *The following electrodes are also usable. ・AGR-801Z (Silver reference combination electrode) ・Combination of AG-311 (Silver indicator electrode) and MS-231Z (Silver reference electrode) ・Combination of AG-311 and RE-241Z (Double junction type silver reference electrode) *Remark The general reference electrode (RE-201Z) cannot be used for this titration because KCl inner solution might come out to sample solution and it causes measurement error. The inner electrodes of AGR-801Z and MS-231Z contain mercury (I) sulfate. When these electrodes are disposed, please ask the specialized industrial waste disposal operator. |
|
| (2) | Reagents | ||
| Titrant | : | 0.01 mol/L Silver nitrate standard solution | |
| Additive solution | : | Diluted nitric acid (1:5, v/v) | |
3. Measurement procedure
| (1) | Dispense 100 mL of sample into a 200 mL beaker with volumetric pipette. |
| (2) | Add 1 ml of diluted nitric acid. |
| (3) | Immerse electrode and start titration with 0.01 mol/L silver nitrate standard solution. |
4. Measurement conditions and results
Examples of titration conditions

Measurement results
| Number of measurement |
Size (mL) |
Titrant volume(mL) |
Chloride ion (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 4.739 | 16.968 |
| 2 | 100 | 4.741 | 16.975 |
| 3 | 100 | 4.737 | 16.961 |
| Statistic calculation |
Avg. | 16.97 ppm | |
| SD | 0.0070 ppm | ||
| RSD | 0.04 % | ||
Example of titration curve

5. Note
| (1) | Measurement The chlorides in tap water was accurately determined by Mohr method with potentiometric titration instead of color indicator titration. |
| (2) | pH of sample When the sample contains hydroxide ion or carbonate ion, they react with silver nitrate titrant and generate silver hydroxide or silver carbonate. It slightly causes positive error on titration for chloride ion. Therefore this titration is generally performed at acidic pH adjusted to pH 2 ~ 3 by nitric acid. |
| Keywords: | Tap water, Chloride ion, Precipitation titration, Silver electrode, Nitric acid |
*Some measurement would not be possible depending on optional configuration of system.