| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Automatic Titrator | Data No. | M9 | Apr. 19, 2018 |
| Resins, Oils and Fats, Rubber, Adhesives, Paints | Determination of isocyanate (NCO) content in adhesives |
1. Abstract
Synthetic adhesives like hydrophilic macromolecule –Isocyanate type wood adhesives are consisted of base compound and cross-linker; the principal components of base compound are macromolecule aqueous solution or aqueous dispersing element, or those combination. The principal components of cross-linker is isocyanate compounds. The measurement procedure of isocyanate (NCO) content described in this report is standardized by JIS K 6806. NCO content is determined by the neutralization titration which excess di-n-butylamine is titrated with hydrochloric acid standard solution after sample and di-n-butylamine are mixed and reacted. A measurement example of potentiometric titration for NCO determination is introduced in this report.
2. Configuration of instruments and reagents
| (1) | Configuration | ||
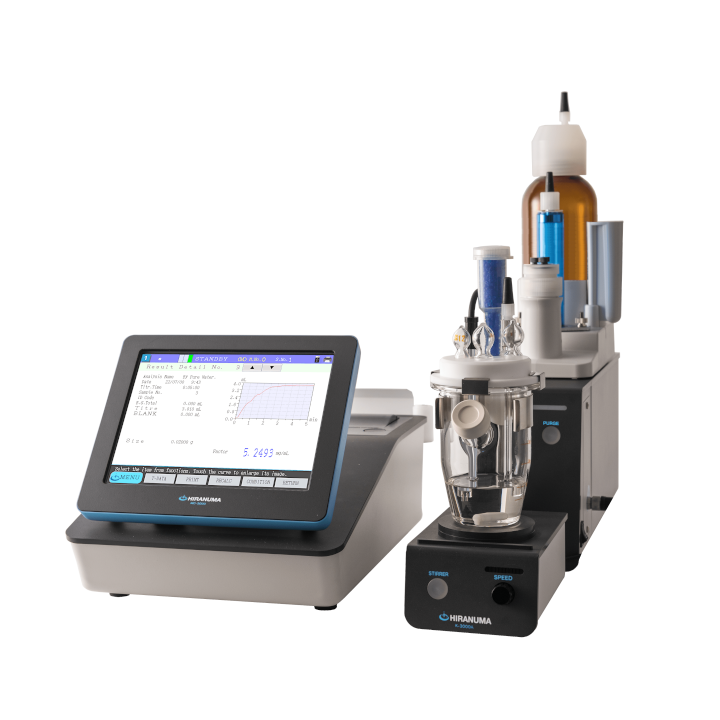
| Main unit | : | Hiranuma Automatic Titrator COM series | |
| Electrode | : | Glass – Reference electrode GR-522BZ | |
| Option | : | Buret tip (Tube Type) | |
| (2) | Reagents | ||
| Titrant | : | 0.5 mol/L Hydrochloric acid standard solution | |
| Solvent | : | 2-propanol (Isopropyl alcohol) | |
| Additive | : | Di-n-butylamine – toluene solution Dissolve 130 g of di-n-butylamine in dehydrated toluene. |
3. Measurement procedure
| (1) | Take about 2 g of the sample into Erlenmeyer flask and accurately weigh it. |
| (2) | Dispense 25 mL of di-n-butylamine – toluene solution with volumetric pipette. |
| (3) | Add stirring bar and close it with a stopper. Gently stir the solution for 15 min with stirrer. |
| (4) | Add 150 mL of 2-propanol. |
| (5) | Immerse the electrode and titrate with 0.5 mol/L hydrochloric acid standard solution. |
| (6) | Measure the blank value by operation of (2) ~ (5) without sample. |
4. Measurement conditions and results
Examples of titration conditions
Measurement of blank
| Cndt No. | 1 | |
| Method | Autot | |
| Buret No. | 1 | |
| Amp No. | 1 | |
| D. Unit | pH | |
| S-Timer | 5 | sec |
| C.P. mL | 45 | mL |
| T Timer | 0 | sec |
| D.P. mL | 0 | mL |
| End Sens | 1000 | |
| Over mL | 0.3 | mL |
| Max.Vol. | 60 | mL |
| ConstantNo. | 1 | |
| Size | 0 | g |
| Blank | 0 | mL |
| Molarity | 0.5 | mol/L |
| Factor | 1.005 | |
| K | 0 | |
| L | 0 | |
| Unit | mL | |
| Formula | D | |
| Digits | 3 | |
|
Auto In Pram.
|
Non | |
| Mode No. | 4 | |
| Pre Int | 0 | sec |
| Del K | 9 | |
| Del Sens | 0 | mV |
| Int Time | 3 | sec |
| Int Sens | 3 | mV |
| Brt Speed | 2 | |
| Pulse | 40 |
Measurement of sample
| Cndt No. | 2 | |
| Method | Auto | |
| Buret No. | 1 | |
| Amp No. | 1 | |
| D. Unit | pH | |
| S-Timer | 10 | sec |
| C.P. mL | 27 | mL |
| T Timer | 10 | sec |
| D.P. mL | 0 | mL |
| End Sens | 1000 | |
| Over mL | 0.3 | mL |
| Max.Vol. | 60 | mL |
| ConstantNo. | 2 | |
| Size | 2.0412 | g |
| Blank | 50.196 | mL |
| Molarity | 0.5 | mol/L |
| Factor | 1.005 | |
| K | 42.02 | |
| L | 0 | |
| Unit | % | |
| Formula | (B-D)*K*F*M/(S*10) | |
| Digits | 4 | |
|
Auto In Pram.
|
Non | |
| Mode No. | 4 | |
| Pre Int | 0 | sec |
| Del K | 9 | |
| Del Sens | 0 | mV |
| Int Time | 3 | sec |
| Int Sens | 3 | mV |
| Brt Speed | 2 | |
| Pulse | 40 |
Measurement results
| Number of Measurements |
Size (g) |
Titrant volume (mL) |
NCO content (%) |
Statistical calculation results |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 1 | – | 50.178 | – | Avg. (Blank) |
50.196 mL |
| 2 | – | 50.214 | – | |||
| Sample | 1 | 2.0412 | 32.105 | 18.714 | Avg. | 18.74 % |
| 2 | 2.0429 | 32.035 | 18.771 | SD | 0.0287 % | |
| 3 | 2.0473 | 32.017 | 18.749 | CV | 0.15 % | |
Examples of titration curves
 |
 |
| Measurement of blank | Measurement of sample |
5. Note
| (1) | Dehydrated toluene (less than 50 ppm water content) is used as a solvent to dissolve sample. Please note that the water in solvent causes measurement error because it reacts with isocyanate group. |
| (2) | Electrode which can be directly inserted into Erlenmeyer flask is preferred for this titration. |
| Keywords: | Isocyanates, NCO, Neutralization titration, JIS K 6806, JIS K 1603, JIS K 7301 |
*Some measurement would not be possible depending on optional configuration of system.