| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Automatic Titrator | Data No. | E7 | Nov. 28,2018 |
| PLATING & ETCHING SOLUTION | Determination of Tin (Sn²⁺) in solder plating solution |
1. Abstract
Tin (Sn²⁺) in solder plating solution is determined by redox titration with iodine. Solder plating solution contains Sn (II) ions, Sn (IV) ions, and acids etc. Iodine works as oxidizing agent for stannous ion. Sn (II) ions are readily oxidized by oxygen in the air to be Sn (IV) ions. The measurement environment under carbon dioxide or nitrogen gas could provide reliable results.
| Sn²⁺ + I₂ → Sn⁴⁺ + 2I⁻ |
This report introduces a measurement example that sample is added to solution under carbon dioxide gas generated by the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate, and titrated with iodine titrant.
2. Configuration of instruments and Reagents
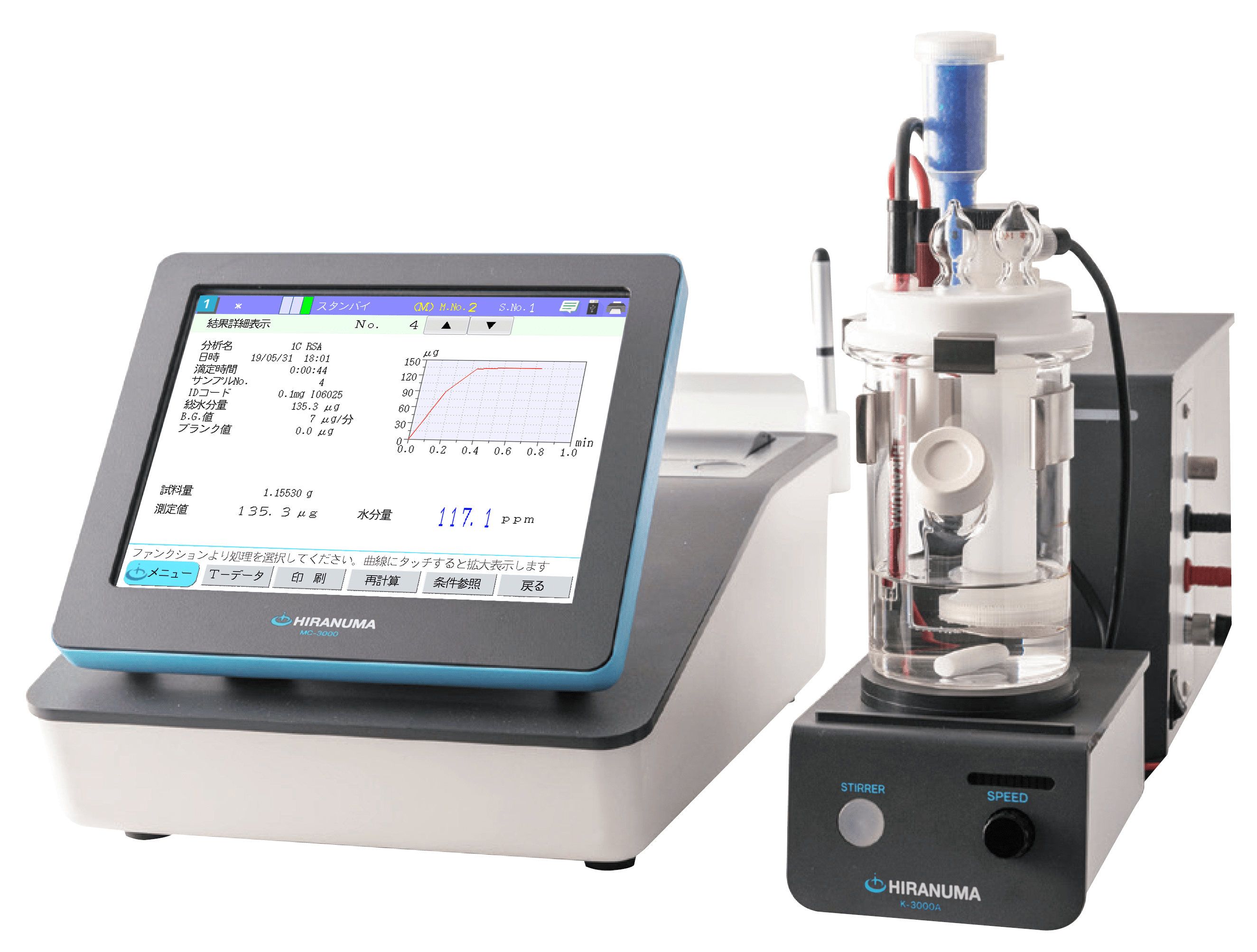
| (1) | Configuration of instruments | ||
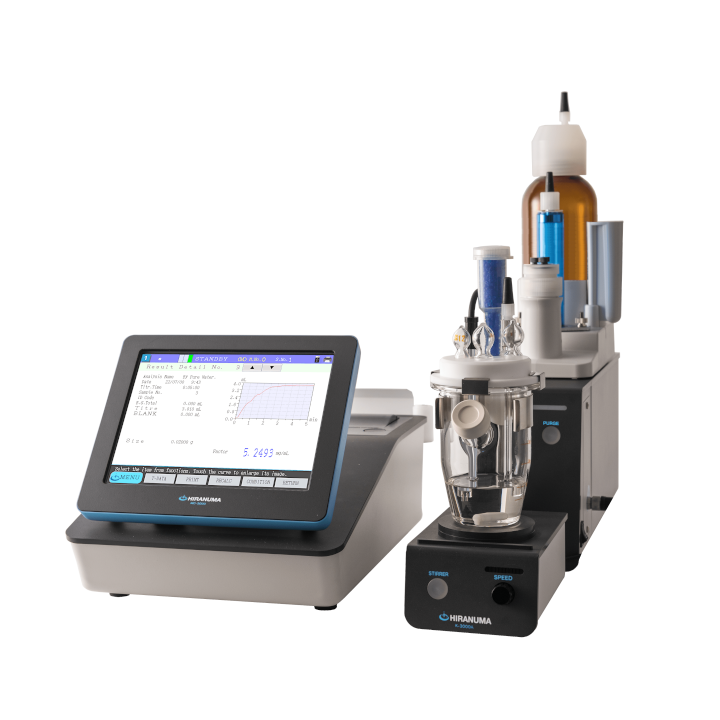
| Main unit | : | Hiranuma Automatic Titrator COM series | |
| Electrodes | : | Platinum electrode PT-301 Reference electrode RE-201Z *The following electrodes are also useable instead of the above electrode. ・PR-701BZ (Platinum reference electrode) ・Combination of PT-301 (Platinum electrode ) and GR-501BZ (Glass-reference electrode) |
|
| (2) | Reagent | ||
| Titrant | : | 0.05 mol/L Iodine standard solution | |
| Additive solution | : | Diluted sulfuric acid 50 mL of sulfuric acid is gently added to 100 mL of DI water. |
|
| : | 5 % Sodium hydrogen carbonate solution Dissolve 25 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate in DI water and diluted to 500 mL. |
||
3. Measurement procedure
| (1) | Take 30 mL of DI water into a 100 mL beaker. |
| (2) | Add 5 mL of diluted sulfuric acid |
| (3) | Carefully add 20 mL of 5 % sodium hydrogen carbonate solution because it foams vigorously. |
| (4) | Add 1 mL of sample into the beaker with volumetric pipette. |
| (5) | Immerse electrodes to start titration with 0.05 mol/L iodine standard solution. |
4. Measurement conditions and results
Examples of titration conditions

Measurement results
| Number of measurement |
Size (mL) |
Titrant volume(mL) |
Sn (II) ion Concentration (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2.376 | 14.200 |
| 2 | 1 | 2.405 | 14.374 |
| 3 | 1 | 2.376 | 14.200 |
| Statistic calculation |
Avg. | 14.3 g/L | |
| SD | 0.1005 g/L | ||
| RSD | 0.70 % | ||
Example of titration curve

5. Note
The following tips could improve measurement accuracy.
| (1) | Influence on air oxidation of Sn (II) ion This titration should be performed under anaerobic environment because Sn (II) ions are readily oxidized by oxygen in the air and its concentration is decreased. The carbon dioxide generated by the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate prevented the oxidation of Sn (II) ions in this report. |
| (2) | Influence of interfering component Solder plating solution contains Sn (IV) ions and acids etc. These components don’t interfere the measurement of Sn (II) ion. However, the reducing agents such as sodium thiosulfate and sodium sulfite react with iodine, it causes positive error. |
| Keywords: | Solder plating solution, Sn (II) ion, Iodine, Redox titration |
*Some measurement would not be possible depending on optional configuration of system.