| HIRANUMA APPLICATION DATA | Automatic Titrator | Data No. | H4 | Apr. 13,2022 |
| SODA PULP INDUSTRY | Determination of available chlorine in sodium hypochlorite |
1. Abstract
Sodium hypochlorite is used for bleaching and sterilization of tap water because of its strong oxidizing and disinfecting properties. Sodium hypochlorite is relatively stable at the alkaline region. However, it is unstable at the acidic region and becomes hypochlorous acid (HClO). It oxidizes water and generates chlorine (Cl2). The concentration of available chlorine has to be measured regularly because sodium hypochlorite degrades slowly and generates sodium chloride.
This report introduces an example for determination of available chlorine as follows:.
1) Add potassium iodide to sodium hypochlorite to generate free iodine.
2) Titrate the free iodine generated from the reaction (1) with sodium thiosulfate to determine available chlorine (2) by redox titration.

2. Configuration of instruments and Reagents
| (1) | Configuration of instruments | ||
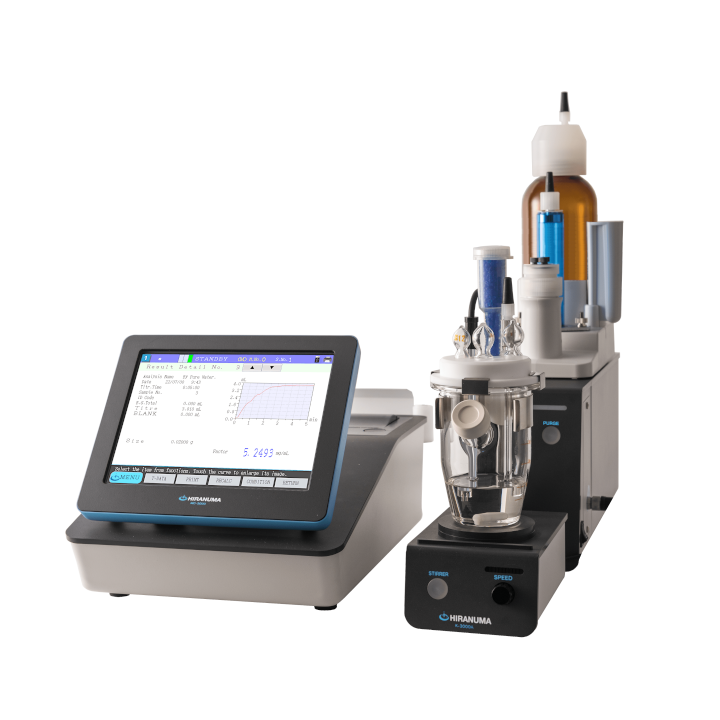
| Main unit | : | Hiranuma Automatic Titrator COM series | |
| Electrode | : | Platinum electrode PT-301 Reference electrode RE-201Z *Instead of above electrodes, the following electrodes are usable. ・PR-701BZ (Platinum reference combination electrode) ・Combination of PT-301 (Platinum Electrode) and GR-501BZ (Glass reference electrode) *Remark Measurement of alkaline component in sodium hypochlorite will be possible with the combination of PT-301 and GR-501BZ. |
|
| (2) | Reagent | ||
| Titrant | : | 0.3 mol/L Sodium thiosulfate standard solution | |
| Additive solution | : | 10 mL of 20% potassium iodide solution | |
| Buffer solution | : | 10 mL of 50 % acetic acid solution | |
3. Measurement procedure
| (1) | Dispense 2 mL of sample and accurately weigh it. |
| (2) | Add about 10 mL of 20 % potassium iodide solution. |
| (3) | Add about 30 mL of DI water. |
| (4) | Add about 10 mL of 50 % acetic acid solution. |
| (5) | Immerse electrodes and titrate with 0.3 mol/L sodium thiosulfate standard solution. |
4. Measurement conditions and results
Examples of titration conditions
| Cndt No. | 1 | |
| Method | Auto | |
| Buret No. | 1 | |
| Amp No. | 2 | |
| D. Unit | mV | |
| S-Timer | 15 | sec |
| C.P. mL | 0 | mL |
| T.Timer | 0 | sec |
| D.P. mL | 0 | mL |
| End Sens | 200 | |
| Over mL | 1 | mL |
| Max.Vol. | 20 | mL |
| ConstantNo. | 1 | |
| Size | 0 | g |
| Blank | 0 | mL |
| Molarity | 0.3 | mol/L |
| Factor | 1.013 | |
| K | 35.45 | |
| L | 0 | |
| Unit | % | |
| Formula | ||
| (D-B)*K*F*M/(S*10) | ||
| Decimal Places | 4 | |
| Auto input parameter | None | |
| Mode No. | 5 | |
| Pre Int | 0 | sec |
| Del K | 5 | |
| Del Sens | 0 | mV |
| Int Time | 3 | sec |
| Int Sens | 3 | mV |
| Brt Speed | 2 | |
| Pulse | 40 | |
| 0.05 | mL | |
Measurement results
|
Number of measurement |
Size (mL) |
Titrant volume(mL) |
Concentration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
2.6123 |
30.710 |
12.6650 |
|
2 |
2.5984 |
30.528 |
12.6572 |
|
3 |
2.5988 |
30.572 |
12.6735 |
|
Statistic calculation |
Avg. |
12.67 % |
|
|
SD |
0.01 % |
||
|
RSD |
0.06 % |
||
Example of titration curve
5. Note
Please refer to the following points to improve the measurement accuracy.
1) Weigh a sample size quickly because available chlorine is unstable.
2) Titrate free iodine immediately because the iodine generated by addition of potassium iodide readily volatilizes.
Addition of plenty potassium iodide is required because the volatilization of iodine depends on the concentration of the added potassium iodide.
|
Keywords: |
Sodium hypochlorite, Available chlorine, Redox titration |
*Some measurement would not be possible depending on optional configuration of system.